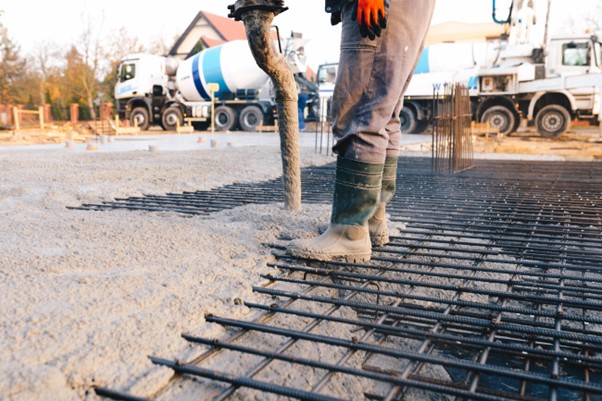
Are you curious about what keeps the grand structures around us intact? How do industrial buildings withstand enormous weight loads and resist potential environmental hazards? The secret lies largely behind an architectural marvel of modern construction – Reinforced Concrete. This blog shall act as your complete guide, illuminating the principles, merits, and considerations around this popular construction material.
Is there an important ingredient holding the concrete construction together? Yes, indeed. Welcome to the world of reinforced concrete, the unsung backbone of our cities’ man-made landscapes. Through this post, we will shine a light on this often overlooked, yet pivotal element of the industrial world’s concreting.
We will explore the intricacies of reinforced concrete, its manufacturing processes, applications, pros, and cons, with an additional highlight on the reasons for its widespread use. Strap in and prepare to deepen your understanding of this essential engineering component.
What is Reinforced Concrete
Reinforced concrete is a composite material where concrete’s robustness and steel’s tensile strength are combined for an optimal result. This amalgamation provides immense durability and longevity, making it an ideal material for industrial concreting.
The strength of this material arises from the concrete providing effective resistance to compressive forces and the steel reinforcements countering the tensile and shear stresses. This synergic relationship makes reinforced concrete a go-to choice for various construction needs.
The ingenious blend of concrete and steel goes beyond mere strength, offering enhanced fire and weather resistance. Pair this with the ease of molding into desired shapes, and you get a material ally that modern architecture counts on.
Why Choose Reinforced Concrete?
There are myriad reasons why reinforced concrete has been the favored choice for industrial use. Not only is it economical, but its flexibility and resilience to seismic activity make it a boon for construction in earthquake-prone regions.
Moreover, the wide availability of its raw materials – cement, aggregate, and steel – ensures a sustainable supply chain, critical for an industry reliant on efficient logistics. The fact that concrete can be poured directly into molds at construction sites further adds to its appeal.
But perhaps, its most appreciated benefit is the enduring lifespan of structures made from reinforced concrete. When properly maintained, these constructs can stand tall for more than a century, testament to its long-lasting nature.
Pros of Reinforced Concrete
Like every construction material, reinforced concrete comes with its set of advantages and disadvantages. Among its benefits, its superior strength, durability, abrasion resistance, and fire resistance stand out. Additionally, it’s more economical, easier to cast and mould, and needs less skilled labor for its construction.
However, on the flip side, reinforced concrete can become susceptible to corrosion if not correctly maintained. Even minor cracks can quickly escalate to more significant problems when not promptly addressed. Moreover, while it’s relatively inexpensive, the costs can escalate with complex designs or when used in colder climates, where special curing methods are required.
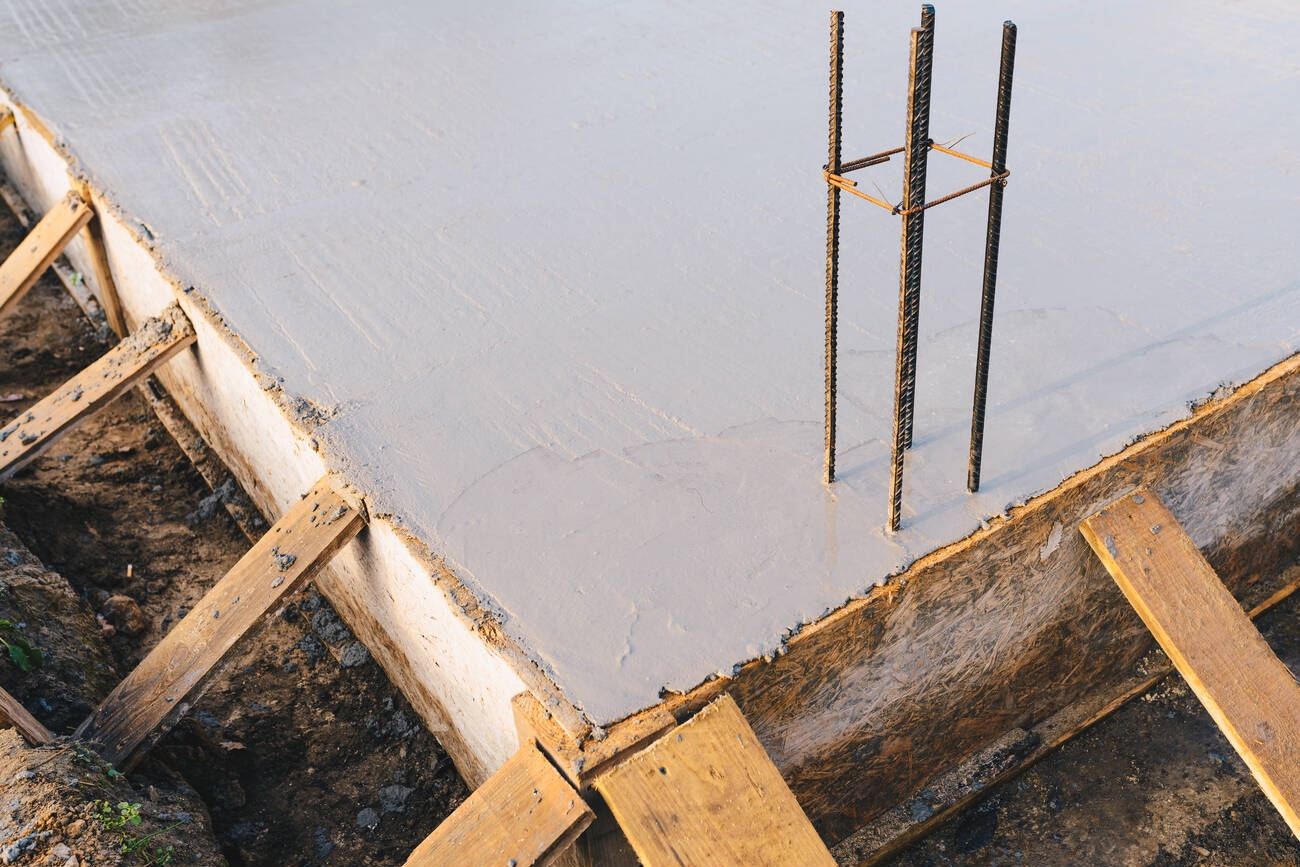

The Art and Science of Making Reinforced Concrete
Creating reinforced concrete requires precision, expertise, and a keen understanding of its fundamentals. The manufacturing process involves mixing concrete – a combination of cement, sand, and coarse aggregate – with water. Reinforcing steel bars, wires, or mesh are then cast into this mix in a specific arrangement, enhancing strength and durability.
Whether the construction project is a towering skyscraper or a humble home, the reinforced concrete mix is poured into molds or ‘formworks,’ which give it the desired shape and size. After curing for a specific period, these molds are removed, revealing structures that promise enduring stability and strength.
The Future Landscape of Reinforced Concrete in Architecture
Given its proven track record and versatility, the future of reinforced concrete in architecture looks promising. With advancements in construction technology and material science, reinforced concrete is evolving, promising to offer even more durability, flexibility, and efficiency in the years to come.
One such advancement is in the realm of ‘High-Performance Concrete,’ offering twice the strength and durability of traditional reinforced concrete. This, coupled with an increased focus on sustainability, promises to shape the approach to industrial concreting.
Conclusion
Without a doubt, reinforced concrete is the mainstay of the architecture and construction world. Its robustness, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and, most importantly, its simplicity of use makes it an attractive proposition. Despite its minor flaws, its wide-ranging advantages continue to make it an indispensable part of our construction landscape.
As we propel ourselves into an era of remarkable architectural feats, it’s precisely these humble foundations that shall continue underpinning our concrete dreams. Therefore, understanding and appreciating the value of reinforced concrete is not just beneficial, but imperative for those shaping our built environment.