Discover the role of swaps in Forex trading, how they work, and why they are important for traders managing overnight positions.
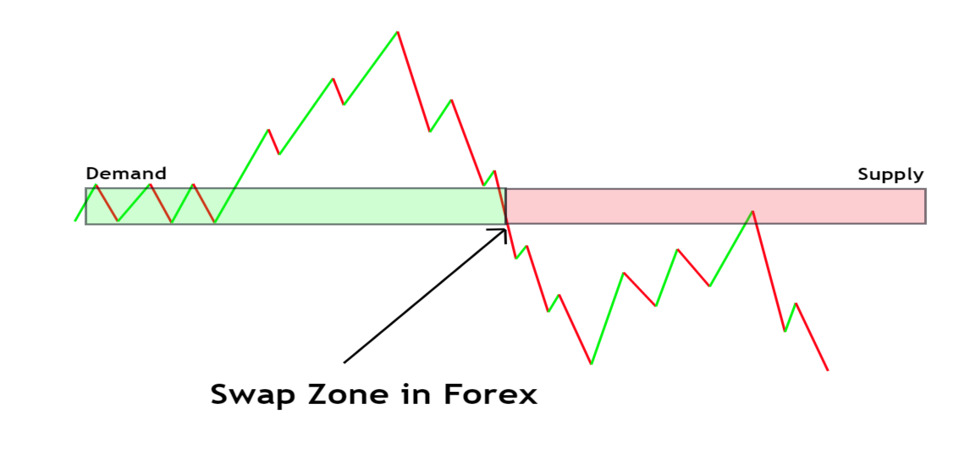
In Forex trading, a “swap” refers to the interest fee that traders pay or earn for holding a position overnight. Swaps are calculated based on the difference in interest rates between the two currencies in a traded pair. Depending on the rate differential, a trader may either gain or lose money from the swap. If you want read more detail about what a swap is check out this article.
Swaps are an essential part of Forex trading strategies, especially for those who hold positions for more than a day. These fees, or credits, play a significant role in defining the long-term cost or benefit of a trade. For instance, when trading a currency pair like EUR/USD, if the euro has a higher interest rate than the dollar, the trader may receive a small profit by holding the euro. Conversely, if the dollar’s rate is higher, the trader will likely incur a fee for holding that position.
Understanding swaps is particularly useful for traders using strategies such as “carry trading,” where they aim to profit from interest rate differences over time. By choosing currency pairs with favorable swap rates, carry traders can build a steady income stream, but they must also factor in the risks, as any currency volatility can quickly affect returns.
In essence, swaps can be both a strategic advantage and an added cost in Forex. For successful trading, it’s crucial to understand how swaps work, assess their impact on overall profit, and choose trades accordingly. Knowing these details helps traders make informed decisions about holding or closing positions, especially if they are considering a long-term strategy.