
Suppose Panther Tees is a t-shirt retailer that sells t-shirts directly to consumers via its online platform. Since the cost of acquiring the products is increasing, the organization wants to determine whether it must increase the price of the t-shirts. Businesses can determine how much (approximately) they can earn or lose in all accounts by taking the revenue percentage relevant to every account and applying it to the forecast number. This method is seen as more reliable because it breaks down the probability of BDE by the length of time past-due. There is a lower chance that recent purchases won’t percentage of sales method be settled by the credit card companies than purchases over a month out. This allows for a more precise understanding of what money may be lost.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question

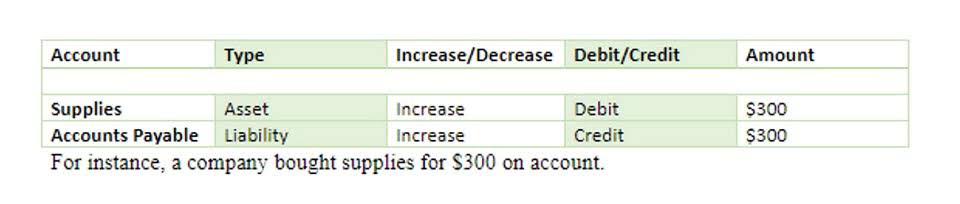
Using data mined from your CRM — along with more in-depth forecasting methods — can help you make more consistent, accurate forecasts. With a revenue of $60,000, she’s not running a corporation, but she should still expect to run into a small amount of bad debt expense. By looking over her records, she finds that for the month, her credit purchases come to $55,000 (with $5,000 cash). To calculate your potential bad debts expense (BDE), simply multiply your total credit sales by the percentage you anticipate losing. The percentage of sales method allows businesses to make accurate assessments of their previous sales so they can comfortably project into the future.
Ask Any Financial Question

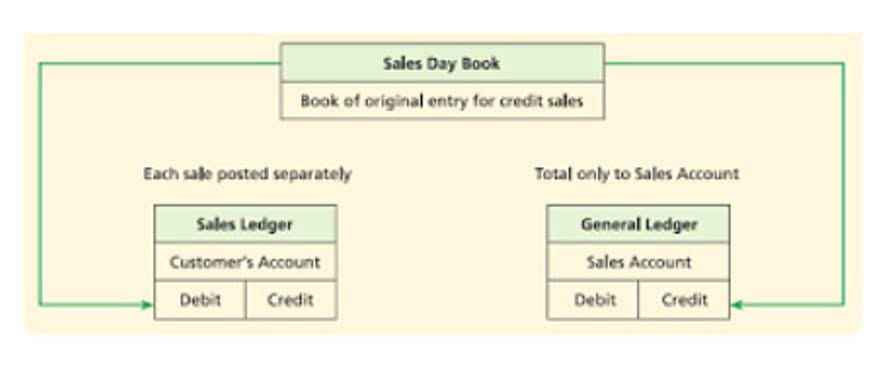
It connects a company’s sales data to income accounts and balance sheets. Although the method cannot provide accurate figures, it still offers businesses an effective way to understand their short-term future from a financial standpoint. The percentage-of-sales method is a financial forecasting model that assesses a company’s financial future by making financial forecasts based on monthly sales revenue and current sales data. Those percentages are then applied to future sales estimates to project each line item’s future value. The percentage of sales method predicts future finances based on current revenue. It looks at financial items like the cost of goods sold (COGS) and accounts receivable as a percentage of your total sales.
- For instance, creditors might compare interest expense to sales to identify whether the company is able to service its debt.
- Each historical expense is converted into a percentage of net sales, and these percentages are then applied to the forecasted sales level in the budget period.
- That’s what we’ll cover in this guide to the percentage-of-sales method.
- It connects a company’s sales data to income accounts and balance sheets.
- At the end of any particular year, the credit balance in this account will fluctuate, but only by coincidence will it be equal to the debit balance in the account Uncollectible Accounts Expense.
- The group can now calculate X to forecast how much money will be available in the following month.
“Percentage of Sales Method” also found in:
Therefore, ROS should be used primarily to compare companies within the same sector rather than across different industries. It also allows for more accurate financial reporting and tax compliance. The balance in the Uncollectible Accounts Expense represents 2% of net credit sales.
- Understanding ROS is key for investors, financial analysts, and management teams aiming to measure a company’s profitability and efficiency.
- We’ll also show you a real-life example, highlighting its benefits and drawbacks.
- The balance in this account will always be a function of a predetermined percentage of credit sales when the net-sales method is used.
- For the sake of example, let’s imagine a hypothetical businessperson, Barbara Bunsen.
- Ultimately, the percent of sales method is a convenient but flawed process of financial forecasting.
Importance of Calculating Return on Sales

Tracking the ratio is helpful for financial analysis as the store might need to change its credit sales policy or collections process if the ratio gets too high. Because the percentage-of-sales method uses common financial ratios and percentages, it’s a good tool for quickly comparing how a company is doing compared to its competitors or the wider market. That also makes it handy for working out in the forecasted financial statements what’s performing well and what isn’t, and by extension setting financial goals for the company.
- The business could run into short-term cash flow problems if the ratio is too high.
- Larger companies allow for a certain percentage of bad credit in their financial analysis, but many small businesses don’t, and it can lead to unrealistic projections and unforeseen loss.
- For instance, total sales for the year were $100,000 and total cost of goods sold was $58,000.
- The Percent of Sales Method involves projecting future financial metrics by applying a consistent percentage to expected sales figures.
- In the absence of this, the management team can identify the costs that are rising and determine whether any cost-cutting measures are necessary.
- Monitoring ROS over multiple periods allows companies and investors to identify trends and evaluate whether a company is improving its profitability or facing challenges.
Liz’s final step is to use the percentages she bookkeeping calculated in step 3 to look at the balance forecasts under an assumption of $66,000 in sales. ROS can sometimes be misleading if the revenue figures are temporarily inflated or operating expenses are artificially reduced. This is why it’s important to look at ROS in conjunction with other financial indicators and trends.
When you can quickly create sales forecasts, you can adapt to sudden storms. Leverage the percentage of sales method to get a clear vision of your financial future so you can map strategies that work. In this step, businesses hope to obtain positive percentages in all accounts. However, the company’s https://www.bookstime.com/ net income is negative if that is not the case. The percentage of receivables method is similar to the percentage of credit sales method, except that it looks at percentages over smaller time frames rather than a flat rate of BDE. ROS is an essential metric for companies looking to assess their profitability at the operational level, and it helps investors compare companies within the same industry.